Smart Water Heaters: The Future of Hot Water Technology for Canadian Homes

Hot water is something most homeowners rely on every day, but few stop to think about how efficiently their water heater is actually working. As home technology continues to evolve, smart water heaters are transforming the way Canadians heat and manage their hot water.
In this guide, we’ll explain how smart water heaters work, explore their key benefits, and help you decide whether upgrading to an energy-efficient water heater is the right move for your home.
- What Are Smart Water Heaters?
- How Smart Water Heaters Work
- Key Benefits of Smart Water Heaters
- Why Smart Water Heaters Make Sense for Canadian Homes
- Smart Water Heaters vs Traditional Water Heaters
- Available Rebates & Incentives for Smart Water Heaters in Canada
- Is a Smart Water Heater Right for Your Home?
- Professional Installation Matters
Ready to upgrade your home’s hot water system? Contact Generations Heating and Air Conditioning today for expert advice and professional smart water heater installation.
Key Takeaways
- Smart water heaters combine advanced sensors, Wi-Fi connectivity, and automation to optimize hot water delivery and energy use.
- They are more energy-efficient than traditional tank or tankless systems, helping reduce utility bills and environmental impact.
- App-based controls allow for remote temperature adjustments, scheduling, usage tracking, and alerts for convenience and peace of mind.
- Smart water heaters are especially beneficial for families, busy households, energy-conscious homeowners, and smart home enthusiasts.
- Proper professional installation is essential for efficiency, safety, and seamless integration with smart home technology.
- Many smart water heaters are eligible for provincial and utility rebates in Canada, particularly ENERGY STAR®-certified or heat pump models.
- Generations Heating and Air Conditioning offers expert guidance, personalized recommendations, and professional installation to ensure reliable performance and long-term savings.
1. What Are Smart Water Heaters?
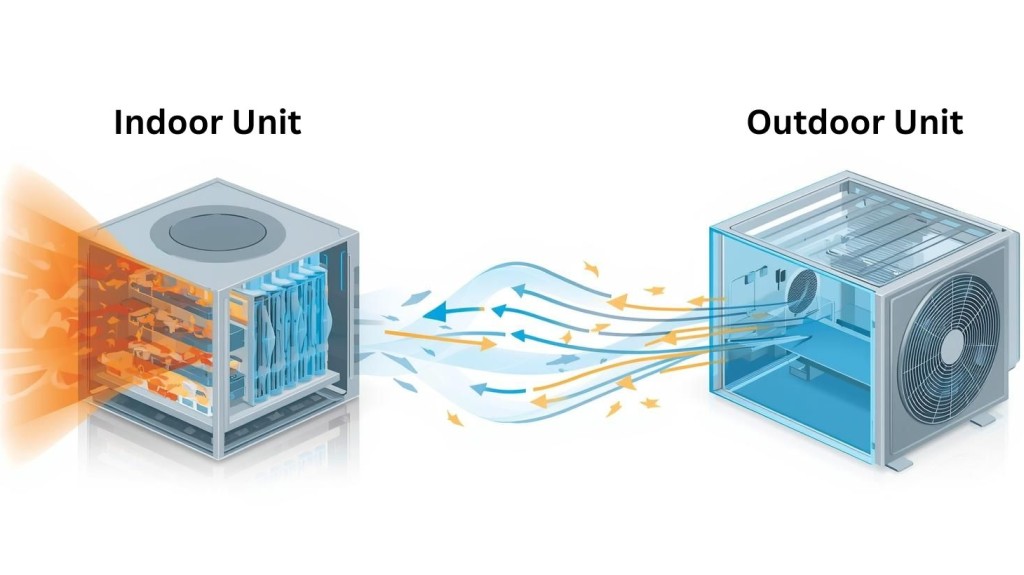
Smart water heaters are a new generation of hot water systems designed to improve efficiency, convenience, and control for homeowners. By combining advanced sensors, internet connectivity, and automated controls, these systems actively manage how and when hot water is heated, rather than simply turning on and off as needed.
Definition of Smart Water Heaters
At their core, smart water heaters use technology to monitor and optimize performance in real time. Unlike conventional systems, they adjust operation based on actual household usage and system conditions.
Key characteristics of smart water heaters include:
- Smart water heaters use built-in sensors to track water temperature, energy consumption, and system performance.
- These systems connect to home Wi-Fi networks, allowing homeowners to monitor and control them remotely.
- Smart controls automatically adjust heating schedules to reduce energy waste while maintaining reliable hot water availability.
Together, these features make smart water heaters a more responsive and energy-conscious solution for modern homes.
How Smart Water Heaters Differ from Traditional Systems
Smart water heaters go beyond the basic functionality of traditional tank and tankless water heaters by adding intelligence and automation. While conventional systems focus solely on heating water, smart models actively manage energy use and performance.
Compared to traditional water heaters:
- Standard tank water heaters continuously heat and store hot water, even when it is not needed, which can lead to higher energy costs.
- Tankless water heaters heat water on demand but lack advanced monitoring, usage tracking, or remote control capabilities.
- Smart water heaters combine efficient heating methods with real-time data and automated decision-making to improve overall performance.
This added intelligence allows homeowners to better control costs and avoid unnecessary energy use.
Built-In Smart Features That Improve Performance
Smart water heaters include a range of advanced features designed to enhance efficiency, convenience, and reliability. These technologies work together to deliver smarter hot water management.
Common built-in smart features include:
- Wi-Fi connectivity that allows homeowners to adjust settings, monitor usage, and receive alerts through a mobile app.
- Advanced sensors that detect temperature changes, water flow, and potential leaks to prevent damage and improve efficiency.
- Automated learning technology that adapts heating schedules based on household hot water usage patterns.
By combining these smart features, smart water heaters represent a significant upgrade in hot water technology, offering Canadian homeowners greater control, improved efficiency, and long-term savings.
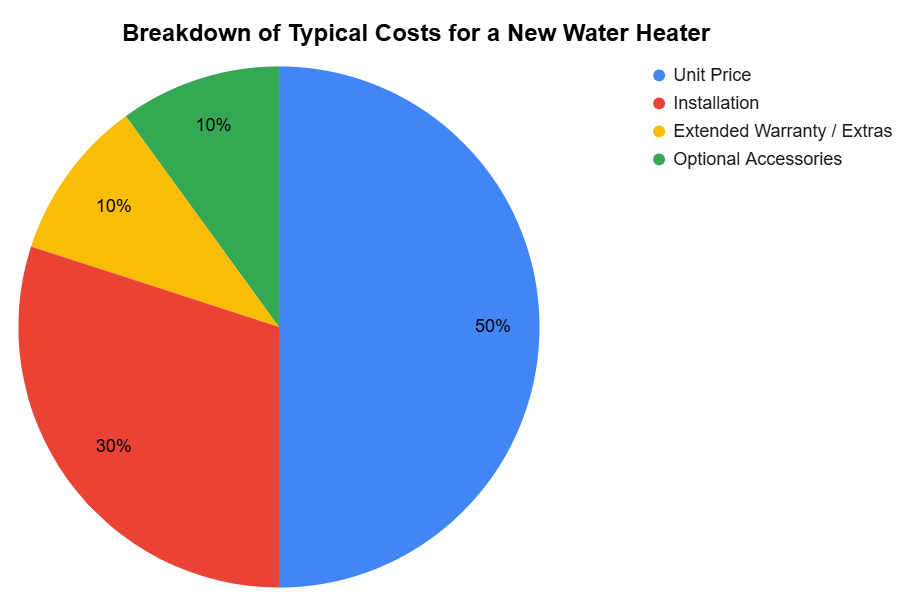
To better understand the potential impact of upgrading, the chart below compares estimated monthly energy costs for a traditional water heater versus a smart water heater over the course of a year. It highlights how adaptive heating, off-peak scheduling, and smarter energy management can lead to noticeable savings over time, especially during high-demand winter months.
2. How Smart Water Heaters Work
Smart water heaters use a combination of sensors, connectivity, and automation to manage hot water more efficiently than traditional systems. Instead of operating on a fixed schedule, these systems continuously collect data and adjust performance to match your household’s actual needs.
Sensors That Monitor Usage, Temperature, and Performance
Smart water heaters rely on advanced sensors to understand how the system is operating at all times. These sensors provide the data needed to improve efficiency and reliability.
Key sensor-driven functions include:
- Sensors that monitor water temperature to ensure consistent and comfortable hot water delivery.
- Usage sensors that track when and how much hot water your household consumes throughout the day.
- Performance sensors that identify inefficiencies or irregular operation before they turn into major problems.
By constantly monitoring these factors, smart water heaters can make real-time adjustments that traditional systems cannot.
Wi-Fi Connectivity and Mobile App Control
Connectivity is what turns a standard water heater into a smart one. Wi-Fi-enabled systems allow homeowners to interact with their water heater remotely using a smartphone or tablet.
Through mobile app integration:
- Homeowners can adjust temperature settings and operating modes from anywhere.
- Real-time energy usage data can be viewed to help manage utility costs.
- System alerts and maintenance notifications can be sent directly to the user’s device.
This level of control makes managing hot water more convenient and energy efficient.
Learning Usage Patterns to Optimize Heating Cycles
Smart water heaters use automation and learning technology to adapt to your household’s routines. Over time, the system recognizes patterns and adjusts heating cycles accordingly.
This adaptive functionality allows the system to:
- Learn peak hot water usage times, such as mornings or evenings.
- Reduce heating during low-use periods to conserve energy.
- Ensure hot water is ready when it is most needed without unnecessary reheating.
As a result, you enjoy reliable hot water while minimizing wasted energy.
Learning Usage Patterns to Optimize Heating Cycles
Many smart water heaters include built-in leak detection features that help protect your home from water damage. These systems monitor for abnormal water flow or moisture around the unit.
Leak protection features typically include:
- Sensors that detect leaks or unusual water movement near the water heater.
- Instant alerts sent to a mobile device when a potential issue is detected.
- Early warnings that allow homeowners to address small problems before they cause costly damage.
This proactive monitoring adds an extra layer of safety and peace of mind.
Integration with Smart Home Ecosystems
Smart water heaters can also connect with popular smart home platforms, allowing for seamless integration into a connected home environment.
Common smart home integrations include:
- Compatibility with platforms such as Google Home and Amazon Alexa for voice control.
- The ability to coordinate with other smart devices to improve overall energy management.
- Centralized control through a single smart home app or dashboard.
By working alongside other smart home technologies, smart water heaters help create a more efficient, convenient, and connected living space.
3. Key Benefits of Smart Water Heaters

Smart water heaters offer you more than just hot water; they combine convenience, energy efficiency, and cost savings into one modern system. By intelligently managing heating cycles and providing real-time insights, these systems help households save money while improving comfort.
Energy Efficiency & Lower Utility Bills
One of the biggest advantages of energy efficient water heaters is their ability to minimize wasted energy while ensuring hot water is always available. Smart water heaters use advanced technology to heat water only when needed, helping homeowners reduce their monthly utility bills.
Smart energy-saving features include:
- Smart controls that automatically reduce unnecessary heating when water is not being used.
- Off-peak scheduling that heats water during lower electricity rate periods, saving on energy costs.
- Adaptive heating technology that learns your household’s routines and optimizes water heating accordingly.
By using energy intelligently, smart water heaters can significantly lower your home’s energy consumption without sacrificing comfort.
Convenience & App-Based Controls
Smart water heaters are designed to give homeowners complete control over their hot water, right from a smartphone or tablet. This convenience makes managing your system effortless and helps prevent unnecessary energy use.
Convenience-focused features include:
- Remote temperature adjustment, so you can ensure hot water is ready when you need it.
- Usage tracking and alerts that notify you of irregular patterns or potential issues.
- Vacation mode and scheduling features that allow you to reduce heating when you’re away from home.
These app-based controls put you in command of your water heater, providing flexibility, efficiency, and peace of mind.
Cost Savings Over Time
Investing in a smart water heater can lead to long-term savings, not just on energy bills but also on maintenance and replacement costs. By proactively monitoring your system, smart water heaters help prevent small problems from becoming costly emergencies.
Cost-saving benefits include:
- Reduced energy consumption thanks to optimized heating cycles and intelligent controls.
- Fewer emergency repairs due to proactive alerts and early problem detection.
- A longer system lifespan as smart features prevent unnecessary wear and tear on components.
Over time, these benefits make smart water heaters a financially wise choice for Canadian homeowners seeking efficiency, reliability, and modern hot water technology.
4. Why Smart Water Heaters Make Sense for Canadian Homes
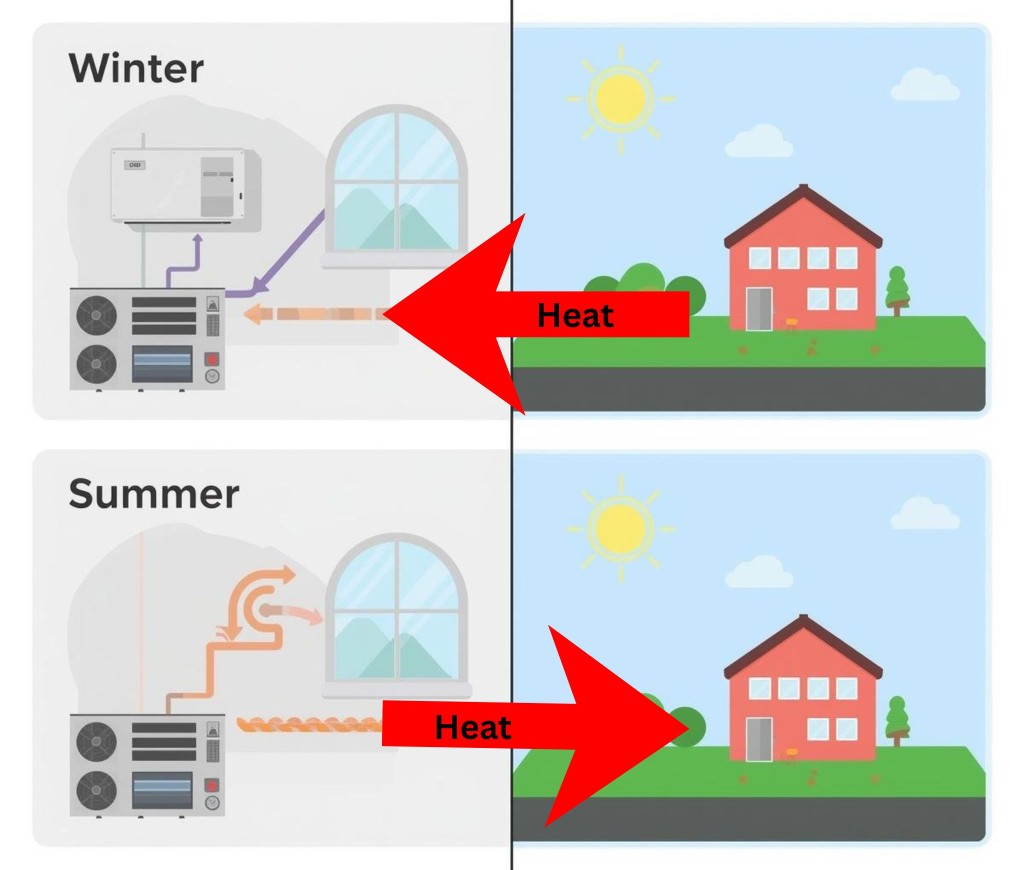
Canadian homes face unique challenges when it comes to heating water, from frigid winter temperatures to high energy costs. Smart water heaters are designed to address these challenges, offering reliable performance, energy savings, and convenience that make them an ideal choice for homeowners across the country.
Reliable Performance in Cold Canadian Climates
Smart water heaters are engineered to maintain consistent hot water even during Canada’s harsh winters. Advanced technology ensures that your household never runs out of hot water, no matter how cold it gets outside.
Performance benefits for cold climates include:
- Smart water heaters maintain consistent temperatures even when incoming water is extremely cold.
- Sensors and adaptive controls adjust heating cycles to meet increased demand during winter months.
- Leak detection and alerts help prevent costly damage caused by frozen pipes or system malfunctions.
With these features, homeowners can enjoy dependable hot water all year long, even in the coldest regions.
Managing High Winter Energy Costs
Electricity and natural gas bills often spike during Canadian winters, making energy efficiency more important than ever. Smart water heaters help reduce unnecessary energy use while keeping your home comfortable.
Energy-saving advantages include:
- Intelligent scheduling heats water during off-peak hours to take advantage of lower utility rates.
- Adaptive heating reduces energy waste by tailoring hot water production to household needs.
- Continuous monitoring allows homeowners to track usage and identify ways to lower costs.
By managing energy intelligently, smart water heaters help you save money while staying warm and comfortable.
Ideal for Families, Rentals, and Busy Households
Households with multiple occupants or varying schedules benefit greatly from the flexibility of smart water heaters. These systems ensure everyone has access to hot water when they need it most.
Convenience benefits include:
- Multiple users can rely on consistent hot water without experiencing shortages.
- Vacation or scheduling modes allow you to reduce energy use when away from the home.
- Smart alerts provide peace of mind in rental properties or busy households by notifying owners of potential issues
This adaptability makes smart water heaters a practical solution for any busy Canadian household.
Compatibility with Various Water Heater Types
Smart technology is not limited to a single style of water heater. Homeowners can enjoy smart functionality with a variety of system types to suit their home’s needs.
Compatibility features include:
- Smart controls can be added to electric, hybrid, and heat pump water heaters.
- Upgrading to a smart system does not require replacing your entire setup in many cases.
- You can select a system that balances efficiency, performance, and installation cost.
By working with multiple types of water heaters, smart systems provide flexibility and long-term value for Canadian homeowners.
Smart water heaters are a modern solution designed to meet the unique demands of Canadian homes, offering energy efficiency, reliability, and convenience that traditional systems simply cannot match.
al solution for any busy Canadian household.
5. Smart Water Heaters vs Traditional Water Heaters
Choosing the right water heater often comes down to understanding how newer technology compares to traditional systems. The table below highlights the key differences between smart water heaters and traditional water heaters, including energy use, control options, monitoring capabilities, and long-term operating costs. This side-by-side comparison makes it easier to see why smart water heaters are quickly becoming the preferred choice for modern Canadian homes.
| Feature | Traditional Water Heater | Smart Water Heater |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Use | Constant heating or on-demand, often inefficient | Adaptive heating based on usage patterns, reduces energy waste |
| Control Options | Manual temperature adjustment | App-based control, schedules, vacation mode |
| Monitoring & Alerts | No monitoring or alerts | Real-time alerts for leaks, temperature, and system performance |
| Long-Term Costs | Higher energy bills, more frequent repairs | Lower energy bills, proactive maintenance reduces repair costs |
When considering a water heater upgrade, it’s important to understand how smart water heaters differ from traditional models. While conventional systems focus on basic hot water delivery, smart water heaters add intelligence, automation, and efficiency that can save you time and money.
Energy Use
One of the most noticeable differences between smart and traditional water heaters is how they manage energy consumption. Smart water heaters are designed to minimize waste and operate more efficiently than older models.
Key energy differences include:
- Traditional tank water heaters continuously heat stored water, which can lead to unnecessary energy use when hot water isn’t needed.
- Tankless systems heat water on demand but lack advanced monitoring, which can result in energy inefficiencies in some households.
- Smart water heaters use sensors and adaptive controls to heat water only when needed, reducing overall energy consumption and lowering utility bills.
By optimizing energy use, smart water heaters deliver a more cost-effective and eco-friendly solution for Canadian homes.
Control Options
Smart water heaters give homeowners unprecedented control over their hot water, while traditional systems offer only basic temperature adjustments.
Control differences include:
- Traditional water heaters rely on manual temperature settings and fixed operation schedules.
- Smart water heaters allow remote temperature adjustments via mobile apps from anywhere in the home or on the go.
- Users can set schedules, vacation modes, and off-peak heating times to match household needs and energy savings goals.
These advanced controls make smart water heaters more convenient and responsive to daily routines.
Monitoring and Alerts
Another major advantage of smart water heaters is their ability to monitor system performance and provide alerts before small issues become major problems.
Monitoring differences include:
- Traditional water heaters provide no real-time feedback on system performance or potential problems.
- Smart water heaters continuously track usage, temperature, and system health.
- You receive alerts for potential leaks, unusual energy usage, or maintenance needs, helping prevent costly repairs.
This proactive monitoring enhances reliability and protects both your home and investment.
Long-Term Operating Costs
While smart water heaters may have a higher upfront cost than traditional units, their energy savings and reduced maintenance can lead to lower long-term operating costs.
Cost comparisons include:
- Traditional water heaters can incur higher energy bills due to constant heating and inefficiencies.
- Older systems may require more frequent repairs or early replacement due to wear and tear.
- Smart water heaters reduce energy consumption, prevent damage through alerts, and often have longer lifespans, providing better value over time.
- Investing in a smart water heater can pay off through both savings and reliability for years to come.
Smart water heaters represent the future of hot water technology. By combining energy efficiency, advanced controls, proactive monitoring, and long-term savings, they offer Canadian homeowners a modern alternative that outperforms traditional water heaters in nearly every way.
6. Available Rebates & Incentives for Smart Water Heaters in Ontario

Upgrading to a smart water heater or other energy‑efficient hot water system can qualify Ontario homeowners for several government and utility rebate programs. While there isn’t always a rebate specifically labeled for “smart water heaters,” many incentives apply to energy efficient water heaters, specially ENERGY STAR®‑rated heat pump and high‑efficiency systems. These rebates can help reduce your upfront costs and improve long‑term energy savings.
Provincial and Utility Rebate Programs in Ontario
Ontario offers several rebate opportunities through provincial and utility programs that support energy‑efficient home upgrades, including water heaters:
- The Home Renovation Savings Program, delivered by Enbridge Gas and Save on Energy with provincial support, offers rebates on qualifying energy‑efficient upgrades, including heat pump water heaters when installed with other eligible improvements.
- Under this program, Ontario homeowners can receive rebates on qualified heat pump water heaters when ENERGY STAR®‑certified models are installed by licensed professionals.
This program is designed to encourage homeowners to reduce energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions while improving home comfort.
Focus on Energy‑Efficient Water Heating Technologies
Although rebates may not specifically mention “smart water heaters,” many of the qualifying systems for Ontario rebates fall into categories that often include smart‑ready or smart‑enabled technology:
- Heat pump water heaters are widely supported by rebate programs due to their high energy efficiency and lower operating costs.
- ENERGY STAR®‑rated electric or tankless water heaters may also qualify for rebates in certain utility streams when installed professionally.
- Rebates often require ENERGY STAR® certification, which ensures that the system meets rigorous energy‑efficiency standards and may include advanced features like smart controls.
Because smart water heaters frequently incorporate ENERGY STAR® certification and operate with greater efficiency, they are well‑aligned with programs aimed at promoting energy savings.
Check Your Local Eligibility
Rebate programs and eligibility criteria can change over time, and availability may vary depending on your local utility, home type, and installation details:
- Always verify current rebate offerings with your utility provider or provincial energy office before purchasing or installing a new system.
- Confirm that your chosen water heater model is ENERGY STAR®‑certified and that professional installation requirements are met to qualify for rebates.
- Some rebates may require a home energy assessment or documentation from a licensed contractor, so planning ahead can help ensure you receive all available incentives.
Taking these steps can help you make the most of current rebate opportunities and maximize savings on your upgrade.
How Generations Can Help You Navigate Rebates
Generations Heating and Air Conditioning stays up to date on the latest rebate programs that apply to energy efficient water heaters and high‑efficiency hot water systems in Ontario. We can help you understand which incentives you may qualify for, assist with proper documentation, and ensure your installation meets rebate requirements. Contact us for expert guidance and to make your smart water heater upgrade as cost‑effective as possible.
Long-Term Operating Costs
While smart water heaters may have a higher upfront cost than traditional units, their energy savings and reduced maintenance can lead to lower long-term operating costs.
Cost comparisons include:
- Traditional water heaters can incur higher energy bills due to constant heating and inefficiencies.
- Older systems may require more frequent repairs or early replacement due to wear and tear.
- Smart water heaters reduce energy consumption, prevent damage through alerts, and often have longer lifespans, providing better value over time.
- Investing in a smart water heater can pay off through both savings and reliability for years to come.
Smart water heaters represent the future of hot water technology. By combining energy efficiency, advanced controls, proactive monitoring, and long-term savings, they offer Canadian homeowners a modern alternative that outperforms traditional water heaters in nearly every way.
7. Is a Smart Water Heater Right for Your Home?
Smart water heaters offer a range of benefits, but deciding whether one is the right choice for your home depends on your household’s needs, lifestyle, and existing infrastructure. Evaluating who will benefit most, as well as important installation considerations, can help you make an informed decision.
Not every home has the same hot water needs. The table below shows which types of homeowners benefit most from smart water heater technology and why it may be a smart upgrade for your household.
| Homeowner Type | Why a Smart Water Heater Is a Good Fit |
|---|---|
| Families | Provides consistent hot water during peak usage times while reducing unnecessary energy use. |
| Energy-Conscious Homeowners | Uses adaptive heating and scheduling to lower utility bills and improve efficiency. |
| Smart Home Users | Integrates with apps, Google Home, or Alexa for convenient remote control and automation. |
| Busy Households | Offers scheduling, alerts, and vacation modes that reduce manual adjustments and worry. |
| Rental Property Owners | Provides leak alerts and performance monitoring to help prevent costly water damage. |
Who Benefits Most from a Smart Water Heater
Certain households gain the most value from smart water heater technology. By understanding these scenarios, you can determine whether a smart system fits your lifestyle.
Homeowners who benefit the most include:
- Families with multiple members or high hot water demand, who need consistent supply throughout the day.
- Energy-conscious homeowners looking to reduce utility bills and environmental impact through energy efficient water heaters.
- Smart home users who want the convenience of controlling temperature and settings remotely through mobile apps or voice assistants.
For these groups, a smart water heater can offer both financial savings and improved convenience, making it a practical upgrade for modern homes.
Considerations Before Installing a Smart Water Heater
Before making the switch, it’s important to consider factors that may affect the installation and operation of your new system.
Key considerations include:
- Upfront cost, which can be higher than traditional water heaters but is often offset by long-term energy savings.
- Electrical requirements, since some smart and heat pump water heaters may need dedicated circuits or higher voltage.
- Wi-Fi access, which is necessary for app-based controls, remote monitoring, and receiving alerts.
Evaluating these factors ensures that your home is ready for a smart water heater and that you’ll enjoy all its benefits without surprises.
Importance of Professional Assessment
A professional assessment is essential to determine the best smart water heater for your home and to ensure it is installed safely and efficiently.
Professional assessment benefits include:
- Confirming that your home’s electrical system can support the water heater’s requirements.
- Recommending the right size and type of system based on your household’s hot water usage.
- Ensuring proper installation to maximize energy efficiency, maintain warranty coverage, and integrate with smart home features.
Working with an experienced contractor guarantees that your investment in a smart water heater delivers reliable performance, long-term savings, and peace of mind.
8. Professional Installation Matters

Installing a smart water heater is more than just replacing an old unit. To ensure your system operates efficiently, safely, and integrates seamlessly with your smart home, professional installation is essential. Expert setup maximizes the performance of your energy efficient water heater and helps you get the most value from your investment.
Why Smart Water Heaters Require Expert Installation
Smart water heaters include advanced technology and require precise installation to function correctly. Proper installation ensures reliability, safety, and long-term efficiency.
Key reasons professional installation matters:
- Smart water heaters involve electrical, plumbing, and sometimes high-voltage connections that must meet safety standards.
- Improper installation can compromise efficiency, reduce lifespan, or void warranties.
- Correct setup is essential for integrating smart features like Wi-Fi connectivity, app controls, and voice assistant compatibility.
Working with a licensed professional eliminates common installation issues and ensures your system operates as intended.
Proper Setup for Efficiency, Safety, and App Integration
A properly installed smart water heater delivers maximum performance while providing convenience and peace of mind.
Benefits of professional setup include:
- Ensuring optimal placement and connection to your home’s plumbing and electrical systems.
- Calibrating temperature settings and heating cycles for energy efficiency and consistent hot water supply.
- Configuring app integration so you can control your water heater remotely and receive alerts for maintenance or issues.
This thorough setup helps you enjoy all the advanced features of your smart water heater without headaches or interruptions.
Ongoing Maintenance and Support
Smart water heaters are designed for longevity, but like all complex systems, they require occasional maintenance. Professional support ensures your system continues to operate efficiently over time.
Maintenance advantages include:
- Routine inspections and servicing to maintain energy efficiency and prevent costly repairs.
- Troubleshooting alerts or malfunctions detected by your smart water heater.
- Guidance on upgrades or adjustments to match changes in household usage or energy-saving goals.
Generations Heating and Air Conditioning offers ongoing maintenance and support, giving you confidence that your system will perform reliably year after year.
Why Choose Generations for Your Smart Water Heater
As local experts in energy efficient water heaters and modern hot water solutions, Generations provides personalized recommendations and professional installation tailored to your home. Our team has extensive experience with smart systems and can help you select the right unit for your household.
Ready to Upgrade?
Ready to upgrade to a smarter, more efficient hot water system? Contact Generations Heating and Air Conditioning to:
- Book a consultation with our experienced team.
- Explore the best smart water heater options for your home.
- Receive professional installation and guidance on maximizing energy savings and convenience.
Take the first step toward reliable, efficient, and modern hot water. Schedule your consultation with Generations today.”
Contact Generations for All Your Home Comfort Needs

Reasons to Choose Generations:
If it's the comfort of your house that you're concerned about, you want to work with a company you can trust. At Generations Heating & Air Conditioning, we pride ourselves on offering professional advice, honest service, and dependable help from start to finish.
Local Experts Serving Kitchener and Beyond
We know Kitchener's weather and home styles inside and out. Our recommendations are based on hands-on experience here, not guesswork.
Friendly, Knowledgeable Technicians
Our service pros are highly trained technicians who care about you and your home. We take the time to clearly explain your options and answer your questions so that you feel confident making every decision.
No Pushy Sales Tricks, Just Honest Advice
You'll never be pressured into buying something you don't need. We prioritize what's best for you and your home, not what's easiest to sell.
Start-to-Finish Service
From the moment you receive your quote to long after your new system is installed, we're with you. Expect clear communication, tidy work, and follow-up service you can trust.
Ready to experience the Generations difference? Book a free consultation today and get the best home comfort for your needs and budget.
What Our Customers Are Saying...
"I would like to express my sincere appreciation for the excellent services provided by Generations Heating to me and my family. I highly recommend their services, as they consistently demonstrate professionalism, and the quality of their work is truly outstanding."
-Jeff Chircop
"We trust Generations to maintain our HVAC system. Their service is prompt, professional, and friendly. They are also very genuine when it comes to purchases, explaining the pros and cons of each model, with zero pressure/upselling.
If you’re looking for an honest, reliable HVAC company that genuinely cares about its customers, then Generations fits the bill."
-Michele A.
"These guys are top notch. I had an issue of no heat due to my error (humidifier issue) that occurred after hours. They called me back within an hour to problem solve the issue and sent a technician first thing in the morning to ensure all was well. Maintenance performed at a reasonable price. Courteous and professional team. Highly recommend."
-Kris Pryke